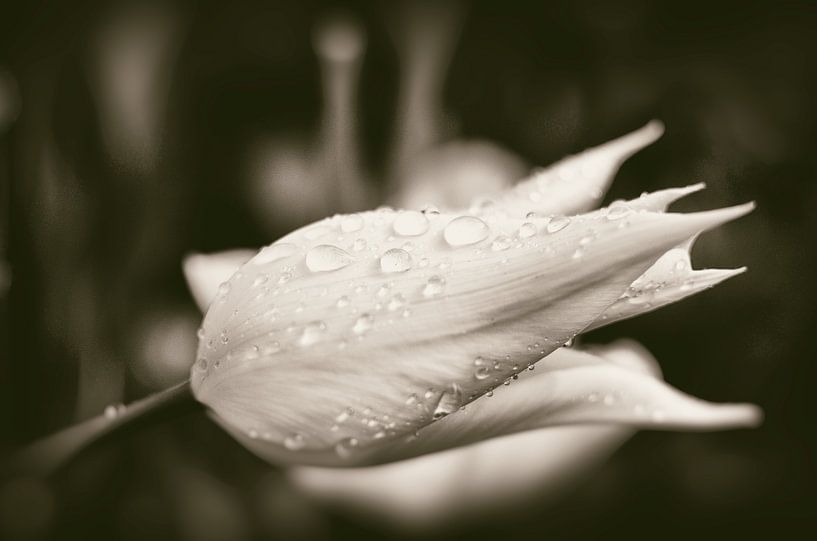
Buy the photo White tulip (monochrome) by Hans Heemsbergen on canvas, ArtFrame, poster and wallpaper, printed on demand in high quality.
About "White tulip (monochrome)"
by Hans Heemsbergen
About the artwork
Tulips need a cold night and a cold winter to grow, so they cannot be grown in warm climates.
Tulip bulbs are usually planted in October and November. The flowering period runs from April into June. A special type of cultivated tulips are the 'botanical tulips' (also known as wild tulips), short-stemmed tulips that also come out the years after the planting year.
Growing new bulbs is done by planting tulip bulbs in the autumn (October and November). The buds between the bulb skirts of these bulbs grow into new bulbs using the old bulb as food. The bud next to the growing point, known as the a-bud, grows into a large bulb that can be sold for flower production or directly to consumers. In addition to the a-bud, the planted bulb contains, between its bulb skirts, more small growth buds, called b-, c-, d- and e-buds, which grow into small bulbs (clisters). These glands are attached to the large bulb, and are removed from the large bulb during summer peeling (removing the roots and old skin of the bulb). In the following autumn, they are planted in the field to grow into large bulbs. In this way, a batch of tulips is maintained: the large bulbs are used for flower production or sold directly to consumers and the small bulbs are planted in autumn. Over 75% of cultivated tulip bulbs are destined for flower production in b

About Hans Heemsbergen
"It is part of the photographer's job to look more intensely than most other people. It is the attitude of a child seeing the world for the first time or of a traveller visiting a foreign land."
Bill Brandt, English photographer (1904 - 1983)..
Read more…
 Germany
Germany Ordered in June 2020
Ordered in June 2020
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in May 2017
Ordered in May 2017

 Germany
Germany Ordered in January 2023
Ordered in January 2023
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2018
Ordered in January 2018
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2020
Ordered in January 2020
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in February 2021
Ordered in February 2021
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in May 2017
Ordered in May 2017
 Germany
Germany Ordered in November 2023
Ordered in November 2023
 Germany
Germany Ordered in September 2021
Ordered in September 2021
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2022
Ordered in January 2022
 Germany
Germany Ordered in October 2021
Ordered in October 2021
 Germany
Germany Ordered in November 2019
Ordered in November 2019
About the material
ArtFrame™
Interchangeable Art Prints
- High-quality print
- Easily interchangeable
- Acoustic function
- Large sizes available
Discover the artworks of Hans Heemsbergen
 There is always hopeHans Heemsbergen
There is always hopeHans Heemsbergen Fan outHans Heemsbergen
Fan outHans Heemsbergen The cartoonist.Hans Heemsbergen
The cartoonist.Hans Heemsbergen DakraamHans Heemsbergen
DakraamHans Heemsbergen Watch and kiteHans Heemsbergen
Watch and kiteHans Heemsbergen PenselenHans Heemsbergen
PenselenHans Heemsbergen BrugmansiaHans Heemsbergen
BrugmansiaHans Heemsbergen Toilet paperHans Heemsbergen
Toilet paperHans Heemsbergen ElsaHans Heemsbergen
ElsaHans Heemsbergen MarjoleinHans Heemsbergen
MarjoleinHans Heemsbergen Dressing gauzeHans Heemsbergen
Dressing gauzeHans Heemsbergen SailorsHans Heemsbergen
SailorsHans Heemsbergen All aloneHans Heemsbergen
All aloneHans Heemsbergen Curious cow 1Hans Heemsbergen
Curious cow 1Hans Heemsbergen Grazing cowsHans Heemsbergen
Grazing cowsHans Heemsbergen Curious cow 2Hans Heemsbergen
Curious cow 2Hans Heemsbergen Minimal artHans Heemsbergen
Minimal artHans Heemsbergen Inspired by Georgia O'KeeffeHans Heemsbergen
Inspired by Georgia O'KeeffeHans Heemsbergen White anemone 02Hans Heemsbergen
White anemone 02Hans Heemsbergen White anemoneHans Heemsbergen
White anemoneHans Heemsbergen













 Elegant Expressions
Elegant Expressions Gentle Whispers
Gentle Whispers Macrophotography
Macrophotography Mysterious Spheres
Mysterious Spheres Photo wallpaper
Photo wallpaper Photography
Photography Rain
Rain Serene Peace
Serene Peace Tulip
Tulip