Buy The Magpie, Claude Monet as a reproduction on canvas, ArtFrame, poster and wallpaper, printed on demand in high quality.
About "The Magpie, Claude Monet"
About the artwork
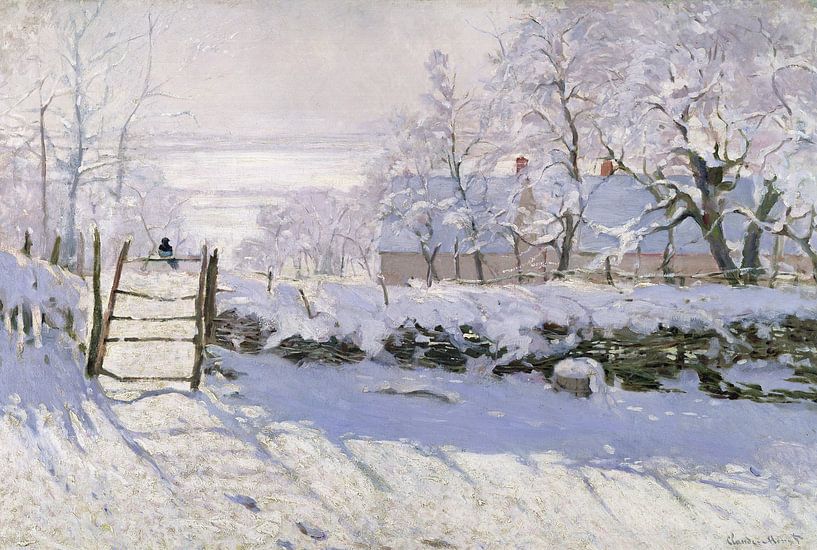
The Magpie, Claude Monet
The Magpie is an oil-on-canvas landscape painting by the French Impressionist Claude Monet, created during the winter of 1868–1869 near the commune of Étretat in Normandy. Monet's patron, Louis Joachim Gaudibert, helped arrange a house in Étretat for Monet's girlfriend Camille Doncieux and their newborn son, allowing Monet to paint in relative comfort, surrounded by his family.
The canvas of The Magpie depicts a solitary black magpie perched on a gate formed in a wattle fence, as the light of the sun shines upon freshly fallen snow creating blue shadows. The painting features one of the first examples of Monet's use of colored shadows, which would later become associated with the Impressionist movement. Monet and the Impressionists used colored shadows to represent the actual, changing conditions of light and shadow as seen in nature, challenging the academic convention of painting shadows black. This subjective theory of color perception was introduced to the art world through the works of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Michel Eugène Chevreul earlier in the century.
At the time, Monet's innovative use of light and color led to its rejection by the Paris Salon of 1869. Today, art historians classify The Magpie as one of Monet's best snowscape paintings. The painting was privately held until the Musée d'Orsay acquired it in 1984; it is considered one of the most popular paintings in their permanent collection.
Old Master collections
Discover more Old Masters in the following collections:
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in April 2019
Ordered in April 2019
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in June 2019
Ordered in June 2019
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in April 2022
Ordered in April 2022
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in October 2018
Ordered in October 2018

 Germany
Germany Ordered in March 2020
Ordered in March 2020
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in March 2022
Ordered in March 2022
 Germany
Germany Ordered in December 2024
Ordered in December 2024
 Germany
Germany Ordered in June 2019
Ordered in June 2019
 Germany
Germany Ordered in December 2019
Ordered in December 2019
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in June 2020
Ordered in June 2020
 Germany
Germany Ordered in March 2019
Ordered in March 2019
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in December 2022
Ordered in December 2022
About the material
ArtFrame™
Interchangeable Art Prints
- High-quality print
- Easily interchangeable
- Acoustic function
- Large sizes available
Discover the Old Masters collection
 Two little girls carrying a basket - Jozef Israels
Two little girls carrying a basket - Jozef Israels Vincent van Gogh, Cornfield with partridge
Vincent van Gogh, Cornfield with partridge The Artist's Garden at Giverny, Claude Monet
The Artist's Garden at Giverny, Claude Monet Henri Matisse. Blue nude
Henri Matisse. Blue nude Francisca Sabasa y Garcia - Portrait woman old master of Francisco Goya
Francisca Sabasa y Garcia - Portrait woman old master of Francisco Goya American Flamingo, original
American Flamingo, original The Tower of Babel, Pieter Bruegel
The Tower of Babel, Pieter Bruegel Woman in a Chemise, André Derain
Woman in a Chemise, André Derain The Tailor, Giovanni Battista Moroni
The Tailor, Giovanni Battista Moroni Oceanides, Akseli Gallen-Kallela
Oceanides, Akseli Gallen-Kallela Bouquet of flowers on white background (seen at VT Wonen)
Bouquet of flowers on white background (seen at VT Wonen) Vincent van Gogh. Sunflowers
Vincent van Gogh. Sunflowers Irma Brunner, Édouard Manet
Irma Brunner, Édouard Manet Portrait of an old man in red, Rembrandt
Portrait of an old man in red, Rembrandt Portrait of a man, anonymous - 1633
Portrait of a man, anonymous - 1633 Self-portrait, Adriaen van de Venne
Self-portrait, Adriaen van de Venne Sunset on the Seine at Lavacourt, Claude Monet
Sunset on the Seine at Lavacourt, Claude Monet Evening prayers, Anna Ancher
Evening prayers, Anna Ancher Rocks by the sea, Paul Gauguin - 1886
Rocks by the sea, Paul Gauguin - 1886 Sunset, Hendrik Willem Mesdag
Sunset, Hendrik Willem Mesdag













 Birds
Birds Claude Monet
Claude Monet Impressionism
Impressionism Landscapes
Landscapes Normandy
Normandy Old masters
Old masters Serene Peace
Serene Peace Snow
Snow Trees
Trees Winter
Winter